This note summarizes key points you need to know before writing classes.
Variables
Primitive Types
- int: integers
- double: decimals
- boolean: true or false
Reference Types
- String
- Objects
The two types are different: Primitive Types store values, Reference Types store address (可以理解为快捷方式?
String 字符串
sequences of characters: letters, numbers, punctuation, spaces…
index: [0, length-1]
String name = "Eileen";- numeric value can be concatenated to a string
- Whenever one of the arguments of the + operator is a string, the other one also becomes a string.
- 括号优先,从左往右算,没有遇到String就按正常的加法算
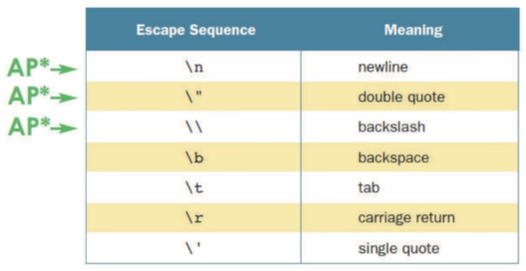
System.out.println(7 + 8 + (7 + 8) + "Hello" + 7 + 8 + (7 + 8)) //the result should be 30Hello7815Escape Sequences 转义字符序列
Compare Strings
- ASCII code: digit< capital letter< lowercase letter
- String 的比较只能使用 .equals() 或者 compareTo(),不要使用 ==!
String Concatenations
- substring 方法的范围截止到 endIndex - 1

Math Class
Math.abs(-3.2)returns 3.2 //returns input typeMath.pow(3, 2.0)returns 9.0 //returns a double regardless of input type; (base, exponent)Math.sqrt(9)returns 3.0 //returns a doubleMath.PI- a public variable of the type double approximately equal to
- Math.random() returns a random number [0,1)
- 要产生一个[k, p]之间的随机整数:
(int)(Math.random()*(p-k+1)+k) - Probability:
- General Rule: Math.random() < probability
- e.g. 40% (2 methods)
- Math.random() < 0.4
- (int)(Math.random()*10)+1 ⇐ 4
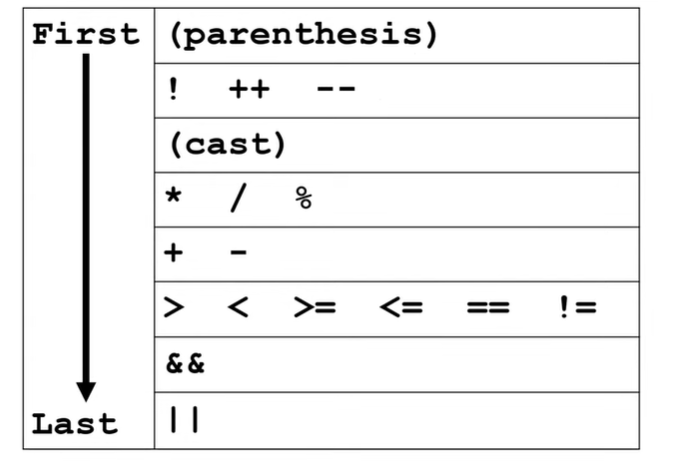
Order of Operation
Boolean Expressions
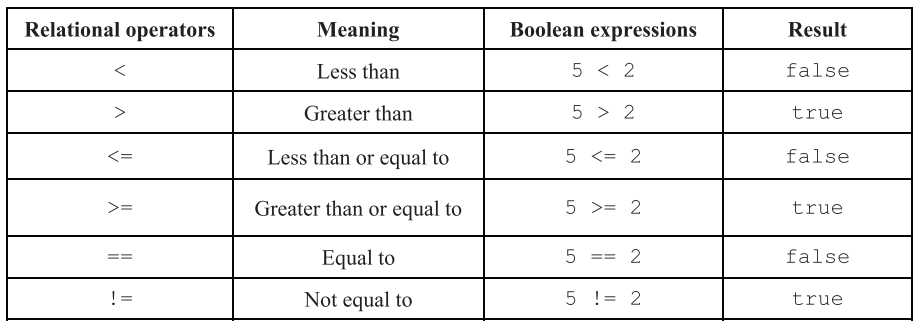
- = is for assignment
- == is for equality testing
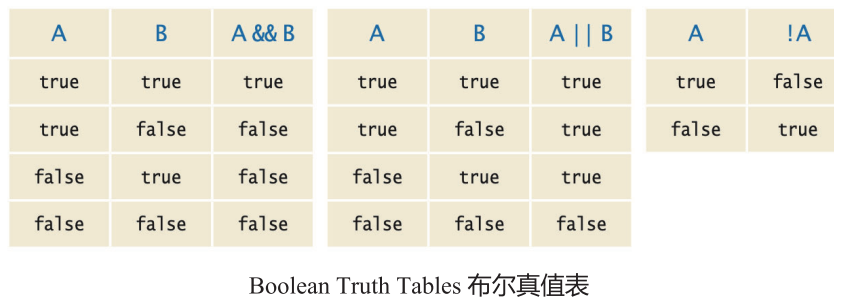
Logical Operators
- && (and 且)
- || (or 或)
- ! (not 非)
- 运算顺序
- arithmetic (+, -, x, /, %)
- relational (e.g. ==)
- logical (先算 && 再算 ||)
- 分配律
- A || (B && C) = (A || B) && (A || C)
真值表
- Applying logical operators
int age = 18;
// if (12 <= age <= 18) // Error
if (age >=12 && age <= 18) // Correct [12,18]- Short-circuited evaluation ^8c5695
- the second boolean value is not reached
- e.g.
false && - e.g.
true || - can be used to avoid NullPointerException
String str = null;
if(str != null && str.length() > 10)
// if(str.length() > 10 && str != null) // you must check null first because if the string itself is null, evaluating "str.length()“ would cause a runtime error
{
System.out.println("something")
}IMPORTANT
De Morgan’s Law 德摩根定理
! (A && B) is the same as !A || !B
! (A || B) is the same as !A && !B
Wrapper Class
- Autoboxing: automatic conversions between primitive values and corresponding wrapper objects
Integer obj3;
int num3 = 69;
obj3 = num3; //automatically creates an Integer object- Unboxing: automatic conversions between wrapper objects and corresponding primitive values
Integer obj4 = new Integer(69);
int num4;
num4 = obj4; //automatically extracts the int valueMethod
Method Overloading
several methods have the same method name with different parameter lists
-
consider:
- number of parameters
- order of parameters
- type of parameters
-
Methods that are exactly the same cannot exist at the same time. (when a method is called, Java decides which version of it to execute depending on the arguments given)
-
return type 是 void 的 method
- 不能用来给变量赋值,return type 和 data type 要对应 (特殊情况是 int 和 double:int 可以给 double 变量赋值,但是 double 不能给 int 变量赋值,因为 double 的范围比 int 大)
- 不能被打印
Iteration 循环
While Loops
- executes statements repeatedly while the condition is true
- avoid infinite loops
- the return statement inside an iteration statement will halt the loop and exit the method or constructor
while (condition)
{
//statements
}For loops
- 可改写成 while loop, while loop 前需要 declaration
for (initialization; condition; update)
{
//statements
}- e.g.
for (int count = 1; count <= 5; count++)
{
System.out.println (count);
Nested Loop
a loop that is declared inside another loop
- each time the outer loop runs once, the inner loop will go through a complete cycle
- 计算次数:
- for (int i = 30; i < 300; i++)
- i: [30, 300) or [30, 299]
- 次数:300-30=270 or 299-30+1=270
If-statements
- if () {}
- if () {} else {}
- if () {} else if {} else {}
- if () {} if () {}
if statements 中,有 else 代表互斥,if 和 else 不能同时执行; 两个 if 代表并列
Common Algorithms
Reverse a String
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str4 = "ap csa";
String temp = "";
for (int k = str4.length(); k > 0; k--) {
temp = temp + str4.substring(k - 1, k);
}
System.out.println(temp);
}