Properties
- all elements have to be reference type
- String
- class
- Integer / Double / Boolean
- size is changeable
- 可以直接打印(array不行)
Declaration
example:
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();Methods
This part is not an exhaustive list of all the methods but a note on important things you should focus on. To see methods that may appear on the test, refer to the Java Quick Reference
add()
valid index: [0, size]
get() and set()
valid index: [0, size - 1]
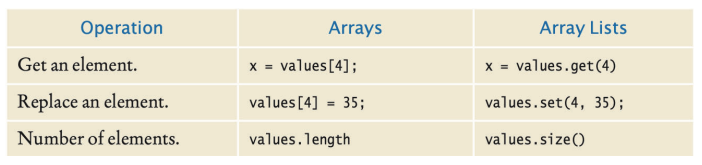
Comparison of String, Array, and Arraylist
| Type | Get the length | Get an element |
|---|---|---|
| String | str.length() | substring(i, i+1) |
| Array | arr.length (this is an attribute, not a method, so no brackets after it) | arr[i] |
| Arraylist | name.size() | get(i) |
Common Algorithms
max and min
- array
double largest = values[0];
for(int i = 1; i < values.length; i++){
if(values[i] > largest){
largest = values[i];
}
}- arraylist
double largest = values.get(0);
for(int i = 1; i < values.size(); i++){
if(values.get(i) > largest){
largest = values.get(i);
}
}deleting elements
Deleting elements during a traversal of an ArrayList requires using special techniques to avoid skipping elements. There are 3 ways:
- if-else
- use while loop cuz the number of loops is not fixed
- if removed, index doesn’t ++ ⇒ check same index (previously at the next index)
- if not removed, move on (index ++)
//remove all strings of length < 4 from an array list
int i = 0;
while (i < words.size()){
String word = words.get(i);
if (word.length() < 4){
words.remove(i);
}
else{
i++;
}
}- i--
- if removed, index —
//remove all strings of length < 4 from an array list
for(int i = 0;i<names.size();i++){
String name = names.get(i);
if(name.length()<4){
names.remove(i);
i--;
}
}- traverse from end to start
//remove all strings of length < 4 from an array list
for(int i = names.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
String name = names.get(i);
if(name.length() < 4){
names.remove(i);
}
}Compare